"I've heard that teeth are related to lifespan, and the number of teeth can indicate how long you'll live."
"Oh? So I don't have many teeth left? Does that mean I don't have many years left to live?"
Lee is 68 years old this year. In the past two years, he has noticed that his teeth have been falling out one after another, and he even feels that his speech is a little lisp. As his teeth continue to fall out, Lee has become very anxious.
Lee was particularly worried after hearing that constantly losing teeth meant a short lifespan. Is tooth loss really related to lifespan?

1. Is there a connection between tooth loss and lifespan? How many teeth should a person have left at age sixty to be considered normal?
The number of permanent teeth in a person is generally between 28 and 32. After the age of 30, the enamel begins to thin and discolor. After the age of 40, the gum tissue begins to shrink due to bacterial invasion. Elderly people may face problems such as loose teeth and tooth loss.
Paying attention to oral hygiene can help reduce tooth loss. According to an epidemiological survey of oral health , the average number of teeth remaining in people aged 65-74 was 20.97 in 2005, which rose to 22.5 in 2016 , and the proportion of people with no teeth also decreased from 6.8% to 4.5%.
The World Health Organization (WHO) proposed the "8020" plan , which states that people aged 80 and older should have at least 20 functional teeth capable of chewing food normally . Studies have found that the number of functional teeth is related to life expectancy. For people over 70 years of age, if they have more than 20 functional teeth , the seven-year mortality risk is 22% . The fewer functional teeth they have, the higher the seven-year mortality risk. If they have zero functional teeth , the seven-year mortality risk can reach 70% .
A 21-year study from Denmark found that people over 70 who lost all their teeth were 2.81 times more likely to become disabled within five years and had a 26% higher risk of death than those with 20 teeth .
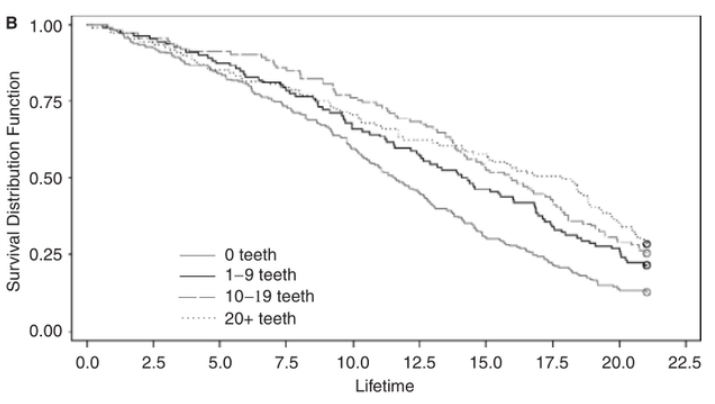
In addition, a Swiss study involving 10,000 middle-aged and elderly participants showed that people with healthy teeth live an average of 11.7 years longer than those with missing teeth .
Second, it is said that people lose their teeth when they get old. Is it a natural phenomenon to lose teeth when you get old?
In the past, most people believed that tooth loss was a natural phenomenon that occurred with age. However, from the perspective of modern medicine , tooth loss in the elderly is not inevitable and may be related to dental problems such as cavities, wear, and periodontitis . The rate at which people lose teeth varies and is generally related to their own health condition and oral hygiene .
Epidemiological surveys of oral health show that only 5% of people aged 55-64 have a healthy periodontal tooth rate, and only 9.3% of people aged 65-75 have a healthy periodontal tooth rate. Many people suffer from dental problems such as periodontitis and tooth decay.
Periodontitis is a very common dental disease that can cause symptoms such as bleeding gums, exposed tooth roots, and loose teeth . In severe cases, it can even lead to tooth loss. Smoking and dental plaque are high-risk factors for periodontal disease.
In addition, dental caries can also cause tooth loss. An epidemiological report on oral health indicates that the incidence of dental caries in people over 60 years old can reach 98% . If dental caries is not treated in time, it may lead to pulpitis or periapical periodontitis, thereby accelerating the premature loss of teeth.
Therefore, tooth loss in the elderly is not an inevitable natural phenomenon. Elderly people who maintain good oral health can still have a good set of teeth. Thus, the key to extending the lifespan of teeth lies in the prevention and control of dental diseases .
III. Four things to extend the "lifespan" of your teeth
The World Health Organization states that healthy teeth are characterized by clean teeth, normal gum color, no pain, no cavities, and no bleeding . To have healthy teeth, it's essential to protect them regularly.
1. Get your teeth checked annually.
Many people lack awareness of oral health prevention. According to the "Survey Report on Dietary and Oral Care Habits of Urban Residents", only 25.7% of residents have their oral health checked 1-2 times a year. It is recommended that everyone have an oral health check at least once a year .
2. Replace your tooth as soon as it falls out.
If you experience symptoms such as loose teeth, widening gaps between teeth, missing teeth, or toothache, it is best to visit a reputable hospital as soon as possible, and cavities should be filled promptly .
3. Maintain proper brushing technique
Develop good brushing habits, ideally brushing both morning and night. When brushing, make sure to clean all areas of your teeth thoroughly to remove plaque and tartar , reducing the risk of periodontal disease, cavities, and other dental problems.

4. Eat chewy foods appropriately.
A diet consisting solely of soft foods can lead to jaw atrophy and make the gums more fragile. It is recommended that middle-aged and elderly people consume some chewy foods to increase the frequency of chewing.
IV. Three types of toothpaste are not recommended for purchase, as they may pose a potential cancer risk.
In addition to paying attention to oral health and developing proper brushing habits, it's also important to choose the right toothpaste. Some toothpastes are not recommended as they may pose a potential carcinogenic risk. A study published in the authoritative international academic journal *Nature Communications* indicated that some toothpastes containing triclosan may harm gut health, induce enteritis, and increase the incidence of related intestinal tumors.
Be wary when buying toothpaste containing these three ingredients, as they may be carcinogenic.
1. Triclosan (TCS)
Triclosan is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent found in many commercial products such as toothpaste, mouthwash, and disinfectants. Triclosan may affect endocrine function; long-term exposure can disrupt thyroid homeostasis, causing metabolic disorders, neurodevelopmental impairments, and may even induce cancer.
2. Benzalkonium chloride (BAC)
Benzalkonium chloride can disrupt the balance of gut microbiota. Experiments have shown that prolonged exposure of animals to low doses of benzalkonium chloride increases the risk of enteritis and colon cancer .
3. Titanium dioxide
Statistics show that 40% of animals that have been exposed to titanium dioxide for a long time have developed precancerous lesions in their intestinal mucosa . Researchers at the French National Institute for Agricultural Research have found that this component may have health effects.
Many people believe that tooth loss is a natural phenomenon of aging. In fact, tooth loss in the elderly is not inevitable. In most cases, it is related to their own health and oral health. It is very likely that dental diseases such as periodontitis and tooth decay accelerate tooth loss.
It is recommended to take preventative measures for oral health and avoid purchasing toothpaste containing ingredients such as triclosan, benzalkonium chloride, and titanium dioxide.