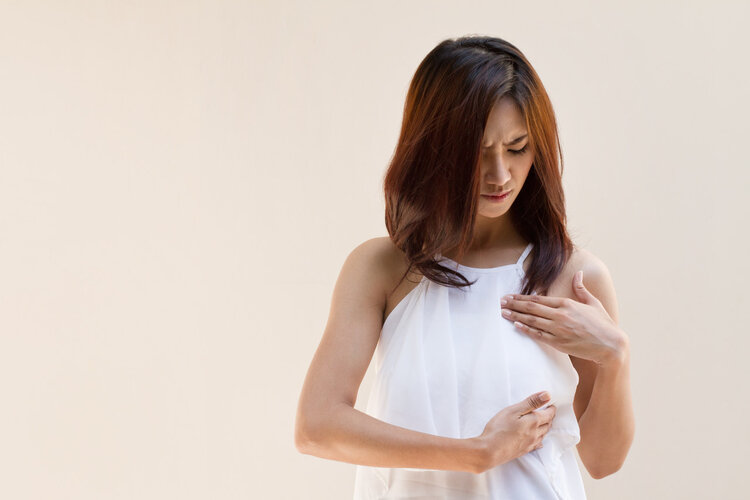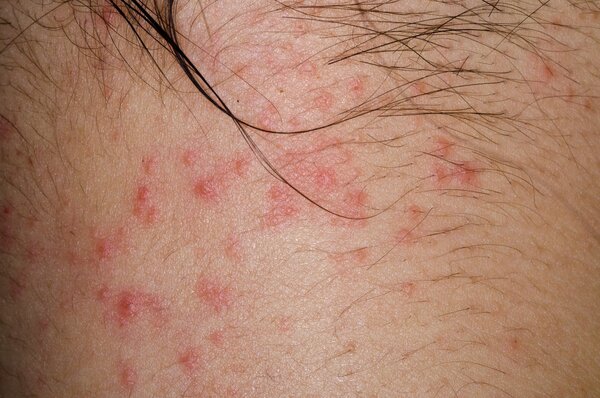
●Allergic skin diseases
People with allergies are prone to allergic skin diseases upon contact with allergens such as pollen and certain foods, experiencing symptoms such as redness, swelling, papules, intense itching, blisters, and peeling. Treatment generally involves oral antihistamines, such as chlorpheniramine, promethazine, loratadine, loratadine, and B vitamins. In addition, appropriate supplements such as vitamin C and calcium gluconate may also be taken. If an allergic reaction occurs on the face, topical medications should not be used indiscriminately; for milder symptoms, cold compresses can be applied.
● Fungal skin diseases
Common fungal skin diseases include tinea capitis, tinea pedis/manuum, onychomycosis, tinea corporis, and tinea cruris. These fungal infections are caused by fungal infections of the skin and hair. Wearing non-breathable shoes and a damp environment are important contributing factors to the development of tinea pedis/manuum.
Most superficial fungal skin diseases can be cured with topical antifungal medications. Some chronic superficial fungal skin diseases require systemic treatment, combining topical medications with oral medications. Currently, the most frequently used antifungal drugs in clinical practice fall into three main categories: polyene macrocyclic compounds, such as amphotericin B and nystatin; alkylamines, such as amorolfine; and imidazoles, such as ketoconazole, miconazole, fluconazole, econazole, and itraconazole. Because the skin affected by tinea corporis and tinea cruris is relatively delicate, milder topical antifungal medications should be selected. Commonly used ones include 1% clotrimazole cream, 2% miconazole cream, or colorless Karl dermatitis ointment. For patients with stubborn or widespread tinea infections, in addition to the above topical medications, short-term oral antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole tablets, one tablet daily for 2–4 weeks, can be used appropriately.
● Contact dermatitis
The majority of patients are women, and the main cause is an allergic reaction to cosmetics or contact with chemicals. Symptoms include facial erythema and blisters, and in severe cases, swelling, pain, and other discomfort.
Treatment may involve oral antihistamines such as chlorpheniramine or loratadine. In severe cases, prednisone or dexamethasone ointment can be applied to the affected area, or the medication can be administered intravenously once daily, generally for no more than a week.
● Pruritus
For patients experiencing generalized itching, a warm bath with calamine lotion once a day can relieve the itching. After bathing, applying a moisturizing skin care product such as camphor cream or petroleum jelly can relieve dryness and itching. When localized itching is severe, never scratch vigorously, as breaking the skin will cause further damage, allowing bacteria to enter and cause inflammation and ulceration. It is best to apply a cold compress with a towel soaked in cool water to relieve the itching.
● Skin eczema
As the weather warms up, some people's hands and feet produce a lot of sweat due to their active sweat glands, especially the feet. If they wear non-breathable shoes for a long time, the hot and humid conditions can cause their feet to peel, itch, and develop blisters. Many people mistake this for athlete's foot, but it is actually eczema.
Treatment options include applying a mixture of vitamin A ointment and urea cream to the affected area, or applying dermatitis ointment to the affected area 1-2 times daily, or soaking hands and feet in lead acetate solution once daily. Foot powder can also be sprinkled on the feet or inside shoes to keep the feet dry. It is important to note that the symptoms of eczema are very similar to those of athlete's foot; if eczema is mistaken for athlete's foot and treated with Daktarin cream, it will not be effective.